Thymine Pharmaceutical Intermediate Pyridines CAS 65-71-4
Thymine Pharmaceutical Intermediate Pyridines |
CAS No.: 65-71-4 |
Purity: ≥98% (HPLC) |
Molecular weight: 126.11 g/mol |
Molecular formula: C5H6N2O2 |
Appearance:White to white crystalline powder |
Package: 1g,10g,100g,1000g |

Thymine Pharmaceutical Intermediate Pyridines CAS 65-71-4
Form:powder
color:white
Storage temp:Sealed in dry,Room Temperature
Stability:Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Laisser un message
Nous vous rappellerons bientôt!
Chère,
Je suis intéressé par Thymine Pharmaceutical Intermediate Pyridines CAS 65-71-4, pouviez-vous m'envoyer plus de détails tels que le type, la taille, le MOQ, le matériel, etc.
Merci !
En attendant votre réponse.
CAS 65-71-4 Thymine Pharmaceutical intermediate Pyridines
Description
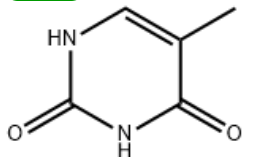
Thymine, also known as 5-methyluracil, is a pyrimidine base, one of the four bases in the nucleotides that form DNA
Basic Parameters
Synonym | Thymine |
MW | 126.11 |
Product category | Pharmaceutical Intermediates |
Melting point | ~320 °C |
Storage condition | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
Structural formula
What is the function of thymine?
Thymine helps stabilize nucleic acid structures. DNA is composed of two strands that twist upon each other to form a double helix. This double helix is held together by hydrogen bonds formed between nucleobases oriented in opposite strands. Adenine forms 2 hydrogen bonds with thymine
What are some interesting facts about thymine?
Thymine is one of the five bases used to build nucleic acids. It is also known as 5-methyluracil or by the abbreviations T or Thy. Thymine is found in DNA, where it pairs with adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil
How does thymine provide stability to DNA?
Thymine at the place of uracil confers to additional stability because thymine has greater resistance to photochemical mutation, making the genetic material more stable. It also forms hydrogen bonds with adenine giving it extra stability.
Why can adenine only pair with thymine?
A always pairs with T and G always pairs with C because these are the only combinations that allow for hydrogen bonding to occur, given the spatial constraints of the double helix, which requires there to be one purine and one pyrimidine in each base pair
Produits recommandés









